Efficiencies from Very High Pt Muons
Proposal of This Page
This are studies performed by Angelo and César on Muon POG. The idea is to compute efficiencies from very high pt muons (out of Z peak) using the
Tag & Probe
method, but with counting numbers instead of a fitting around Z peak.
This log has started on Oct 26th, 2013.
Introduction
Complete

A eficiência com que o detector identifica múons é diferente entre eventos de dados reais e eventos simulados. Atualmente essa eficiência é calculada no CMS com base no chamado método “Tag and Probe”, que permite uma performance significativa na identificação de múons através da análise da massa invariante de dois múons de cargas opostas. Contudo, como as buscas por nova Física têm trabalhado com hipóteses que preveem a existência de partículas cada vez mais massiva, e com o acelerador LHC operando a energias cada vez mais altas, observou-se a necessidade da adequação daquele método aos novos cenários.
O LHC colide feixes de prótons a energias de centro de massa consideravelmente altas. Entre 2009 e 2011, o acelerador gerou, progressivamente, colisões de 900, 2.360 e 7000 GeV de energia no centro de massa, chegando a 8.000 GeV em 2012. Atualmente o LHC não está em operação pois passa por uma fase de atualizações com a finalidade de operar a 14.000 GeV, na retomada de funcionamento em 2015, que é a energia para a qual o acelerador foi inicialmente proposto. Colisões próton-próton a energias de centro de massa dessa magnitude tem como resultado a geração de partículas com altos momentos: da ordem de centenas ou, ainda, de milhares de GeV/c.
O momento transversal (p
T) das partículas carregadas, que atravessam o detector CMS, é calculado a partir da curvatura de suas trajetórias. Essa curvatura é resultante da interação com um campo magnético de 3.8 Tesla (valor no eixo de simetria do detector) gerado por um solenóide supercondutor. Dentre as partículas carregadas, apenas os múons, cuja massa é de 105 MeV/c², conseguem atravessar todo o detector pois são caracterizados por um tempo de decaimento longo (2,2 μs) e depositam apenas uma pequena fração de sua energia nos calorímetros. É possível calcular o p
T de múons pouco energéticos com grande precisão dada a grande curvatura da trajetória que traçam. Por outro lado, a trajetória de múons altamente energéticos desenha um traçado quase retilíneo, diminuindo a precisão na determinação do momento transversal.
O cálculo da eficiência através do método “Tag and Probe” é perfeitamente factível quando os múons estudados apresentam baixos valores de p
T, considerando que a reconstrução da massa invariante de duas partículas de cargas opostas, candidatas a múons, resulta mais frequentemente em ressonâncias com baixos valores de massa como os mésons J/Ψ (3,1 GeV/c²) e ϒ (9,5 GeV/c²), e o bóson Z (91,2 GeV/c²). A presença dessas ressonâncias permite selecionar eventos com pares de múons praticamente isolados de ruído. O método “Tag and Probe” consiste em calcular a eficiência na identificação de múons verificando a probabilidade de um dos candidatos a múon (no par) poder ser observado com o perfil do segundo candidato a múon, o qual possui características mais próximas de um múon verdadeiro.
Múons com altos valores de p
T, por sua vez, têm maior probabilidade de reconstruir massas invariantes acima de 100 GeV/c² e que estão fora da região onde são observadas as ressonâncias, havendo então a necessidade de adequar o método “Tag and Probe”. Angelo Santos e César Bernardes participam ativamente do Grupo de Múons da colaboração CMS e são responsáveis por desenvolver uma técnica de analise de dados, adaptando o método “Tag and Probe” ao novo cenário, a fim de obter eficiências de múons altamente energéticos para eventos de dados reais e de simulação.
Description of The Task
Complete

The standard T&P technique uses known resonances to help in the selection of true muon pairs. Then in this well described region, i.e., in a mass window around this resonance we select a muon candidate with a considerably tight criteria (high probability to be a true muon - called Tag). Since we need two muons to reconstruct the resonance and we know from numerous previous studies the shape of the dimuon distribution we use fits to select a second muon candidate (called Probe), separating with very good precision muons from background and signal(the resonance). Then we have the Probe, a muon candidate with a high probability to be a true muon and without any tight criteria applied so that we can consider any desirable requeriment to extract its efficiency.
It is known that the dimuon mass distribution has some dependency on the pT of each muon of the pair, so that the muons belonging to pairs with high mass tend to have higher pTs. With the constant raise in the energy of LHC proton-proton collisions it becomes more and more important a good knowledge concerning identification criterias for high pT muons. Since the well known resonances pointed above lie in the low (~10 GeV/c^2 ) and intermidiate (~100 GeV/c^2) mass we start to have a considerably loss of these high pT muons candidates to calculate the efficiencies. Even in the case that they enter in the mass window, in the tail of these distributions we have much more difficulties to separate the backgrounds, that start to be considerable given the low statistic in the signal for this region. With this fact in mind our task is to elaborate a T&P procedure with an expansion of the dimuon mass window for values of the order of ~1TeV. Our first try is to not more use fits, instead we work only with counting, then in principle we loose the ability to select a Probe candidate with a high probability to be a "true" muon. In this case we need to estimate very well the background contamination and eliminate it in a good compromise in gaining in signal pairs (mostly Drell-Yan events) so that we can control the systematics.
Setting Up the Tag & Probe method
Complete
 Here
Here
are the first steps to setup the Tag & Probe method using
recipe 8 for
CMSSW_5_3_10. Check
here
on how to set up the code via GitHub.
Commom Settup
Basically do:
cmsrel CMSSW_5_3_10
cd CMSSW_5_3_10/src
cmsenv
cvs co -r V04-04-13 PhysicsTools/TagAndProbe
cvs co -r V02-03-01 MuonAnalysis/MuonAssociators
cvs co -r V08-05-01 MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe
scram b
This version of the
CMSSW code is recommended because the desired
NewTuneP variables (will talk later about) are already implemented as a selector. If using version
CMSSW_5_3_7, one would have to implement those variables by hand.
Main config files to produce Data and MC T&P trees are
Pre-Selection of Events
Here we present the preselection used to produce the current trees:
| Object |
Selection |
| Tag Muon |
pT > 15 GeV/c && Matched in dR<0.1 with the L3Trigger objects && pfIsolationR04().sumChargedHadronPt/pt < 0.2 (charged hadrons not from PU vertices) && Tight2012ID (isPFMuon && numberOfMatchedStations > 1 && muonID('GlobalMuonPromptTight') (global muons with tighter fit requirements) && abs(dB) < 0.2 && track.hitPattern.trackerLayersWithMeasurement > 5 && track.hitPattern.numberOfValidPixelHits > 0) |
| Probe Muon |
pT > 15 GeV/c && track.isNonnull |
| T&P Pair |
abs(Probe.vz - Tag.vz) < 4 cm (vz is the "z" coordinate of the vertice wrt (0,0,0) of the detector) - We DON'T require opposite charge at this level!!! |
| Event |
primaryVertexFilterPath && noscrapingFilterPath |
Variables for Tag & Probe Studies
Complete

Before starting trees production, there is a need to add a set of variables we are interested in. These variables are listed in the table bellow.
| Variables |
Details |
Associated Muons |
Description |
| pT, η, Φ |
|
Tag & Probe |
Used in control plots and to compute efficiencies |
| pT, η, Φ |
From NewTuneP |
Tag & Probe |
Used in control plots and to compute efficiencies, but expecting to be more efficient |
| HighPtID |
From NewTuneP |
Tag & Probe |
True (False) if muons have (not) passed the ID criteria |
| ΔR(μ1,μ2) |
|
T&P pair |
Used in control plots and to compute efficiencies |
| z coordinate, r distance (w.r.t. detector origin) and χ2 / n.d.f |
From vertex fit on T&P muon tracks |
T&P pair |
A tighter upper cut on χ2 / n.d.f. leads to a better momentum description and reduces background |
| x and y distances between vertices of the two muons, and √(Δx2 + Δy2) |
From vertex fit on T&P muon tracks |
T&P pair |
The x and y vertex positions are taken with respect to the detector origin |
| r distance with respect to the beam spot |
From vertex fit on T&P muon tracks |
T&P pair |
Data and MC have different beam spot positions |
| pT of Tag and Probe muons |
Before and after vertex fit on T&P muon tracks |
T&P pair |
Used for comparison purpose |
| collinearity = π - 3D angle |
3D angle between 3-momentum of muons is accounted here |
T&P pair |
Collinearity ≡ α > 0.02 should reduce background from cosmic ray muons |
| Number of vertices |
|
Tag |
Used to reweight MC events and in control plots |
| MET |
|
Tag |
Lower cut on MET reduces QCD background |
| ΔpT/pT |
From inner track fit |
Tag |
ΔpT/pT < 0.1 ensures better quality of momentum and reduces QCD background |
| ∑pT/pT |
Tracker based isolation |
Tag |
Computed later on from already created variables and used in control plots |
| PFCombined isolation |
With beta correction |
Tag |
PFCombined < 0.12 reduces the background |
| pT, η, Φ |
From GenParticles |
GenMuons |
Information from muons in generator level |
| mass(μ1,μ2) |
From GenParticles |
GenMuons |
Information from muons in generator level |
Creating Producers
Complete

Some the variables are include using
ValueMap. It is the case of variables like MET, collinearity and those ones carrying information from vertex fit on muon tracks and from muons in generator level. Variables which use
NewTuneP are included in
UserFloat.
Create producers typing:
cd CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/
cmsenv
mkedprod METProducer
mkedprod VetoCosmicMuonsProducer
mkedprod DimuonVtxProducer
mkedprod GenPVariablesProducer
mkedprod NewTunePMuonsProducer
Next topics explain how to fill out the producers accordingly.
Variable: MET
cd METProducer/
Following this
example
, write the producer
src/METProducer.cc as follows:
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/ValueMap.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/View.h"
#include "DataFormats/Candidate/interface/CandidateFwd.h"
#include "DataFormats/Candidate/interface/Candidate.h"
#include "DataFormats/METReco/interface/PFMET.h"
...
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::InputTag probes_;
edm::InputTag objects_;
...
// constructors and destructor
//
METProducer::METProducer(const edm::ParameterSet& iConfig) :
probes_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("probes")),
objects_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("objects"))
{
...
//now do what ever other initialization is needed
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >();
...
// read input
Handle<View<reco::Candidate> > probes;
Handle<std::vector<reco::PFMET> > objects;
iEvent.getByLabel(probes_, probes);
iEvent.getByLabel(objects_, objects);
// get the PFMET
float met = objects->begin()->et();
// prepare vector for output
std::vector<float> values(probes->size(), met);
// convert into ValueMap and store
std::auto_ptr<ValueMap<float> > valMap(new ValueMap<float>());
ValueMap<float>::Filler filler(*valMap);
filler.insert(probes, values.begin(), values.end());
filler.fill();
iEvent.put(valMap);
Fill
BuildFile.xml including the lines bellow:
<use name="DataFormats/RecoCandidate"/>
<use name="DataFormats/Candidate"/>
<use name="DataFormats/PatCandidates"/>
<use name="DataFormats/METReco"/>
Variable: χ2 of the Vertex Fit for the Tag and Probe Pair
This variable and all related ones are added in a similar way as done for
MET using
ValueMap. The idea is to follow the
recipe
used to implement
GeneralTracks, and also information from
CMSSW WorkBook
, but applying the case of muons concerning the
KalmanVertexFitter method through
TrackRef.
cd DimuonVtxProducer/
Inside
BuildFile.xml, add
<use name="FWCore/Utilities"/>
<use name="DataFormats/Common"/>
<use name="DataFormats/Candidate"/>
<use name="DataFormats/MuonReco"/>
<use name="DataFormats/TrackReco"/>
<use name="FWCore/ServiceRegistry"/>
<use name="CommonTools/UtilAlgos"/>
<use name="TrackingTools/TransientTrack"/>
<use name="TrackingTools/Records"/>
<use name="RecoVertex/KalmanVertexFit"/>
<use name="root"/>
Inside producer
src/DimuonVtxProducer.cc, add the following peaces of code
//my includes
#include "FWCore/Utilities/interface/InputTag.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/ValueMap.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/View.h"
#include "DataFormats/Candidate/interface/CompositeCandidate.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/Muon.h"
#include "DataFormats/BeamSpot/interface/BeamSpot.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/MuonCocktails.h"
//for tracks
#include "DataFormats/TrackReco/interface/Track.h"
// for vertexing
#include "FWCore/Framework/interface/ESHandle.h"
#include "TrackingTools/TransientTrack/interface/TransientTrack.h"
#include "TrackingTools/TransientTrack/interface/TransientTrackBuilder.h"
#include "TrackingTools/Records/interface/TransientTrackRecord.h"
#include "RecoVertex/KalmanVertexFit/interface/KalmanVertexFitter.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <TMath.h>
...
// class declaration
//
class DimuonVtxProducer : public edm::EDProducer {
public:
explicit DimuonVtxProducer(const edm::ParameterSet&);
~DimuonVtxProducer();
static void fillDescriptions(edm::ConfigurationDescriptions& descriptions);
reco::TrackRef mu_track(const reco::Muon & mu);
...
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::InputTag src_;
/// Write a ValueMap<float> in the event
void writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const ;
...
// constructors and destructor
//
DimuonVtxProducer::DimuonVtxProducer(const edm::ParameterSet& iConfig) :
src_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("src"))
...
//now do what ever other initialization is needed
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vtxNormQui2");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vtxZcoordinate");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vtxRdistance");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vtxRdistanceFromBS");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("tagPtAtTheVtx");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("probePtAtTheVtx");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("tagPtBefore");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("probePtBefore");
...
/* this is an EventSetup example
//Read SetupData from the SetupRecord in the EventSetup
ESHandle<SetupData> pSetup;
iSetup.get<SetupRecord>().get(pSetup);
*/
edm::Handle<reco::BeamSpot> recoBeamSpotHandle;
iEvent.getByLabel("offlineBeamSpot" ,recoBeamSpotHandle);
reco::BeamSpot bs = *recoBeamSpotHandle;
math::XYZPoint BSPosition;
BSPosition = bs.position();
Handle<View<reco::Candidate> > src;
iEvent.getByLabel(src_, src);
size_t n = src->size();
std::vector<float> vtxNormQui2(n,-999), vtxZcoordinate(n,-999), vtxRdistance(n,-999), vtxRdistanceFromBS(n,-999), tagPtAtTheVtx(n,0), probePtAtTheVtx(n,0), tagPtBefore(n,0), probePtBefore(n,0);
edm::ESHandle<TransientTrackBuilder> trkBuild;
iSetup.get<TransientTrackRecord>().get("TransientTrackBuilder",trkBuild);
for(size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
const reco::Candidate & ci = (*src)[i];
if (ci.numberOfDaughters() != 2) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") <<
"DimuonVtxProducer should be used on composite candidates with two daughters, this one has " << ci.numberOfDaughters() << "\n";
const reco::Candidate &d1 = *ci.daughter(0), &d2 = *ci.daughter(1);
const reco::Muon *mu1 = dynamic_cast<const reco::Muon *>(&*d1.masterClone());
if (mu1 == 0) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") << "First daughter of candidate is not a ShallowClone of a reco::Muon\n";
reco::Muon::MuonTrackTypePair tuneP1 = muon::tevOptimized(*mu1, 200, 40., 17., 0.25);
const reco::Muon *mu2 = dynamic_cast<const reco::Muon *>(&*d2.masterClone());
if (mu2 == 0) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") << "Second daughter of candidate is not a ShallowClone of a reco::Muon\n";
reco::Muon::MuonTrackTypePair tuneP2 = muon::tevOptimized(*mu2, 200, 40., 17., 0.25);
if( mu1->globalTrack().isNull() || mu2->globalTrack().isNull() ) continue;
if( (mu1->charge() == mu2->charge()) && (tuneP1.first->pt() == tuneP2.first->pt()) ) continue;
reco::TrackRef muon1 = mu_track(*mu1);
reco::TrackRef muon2 = mu_track(*mu2);
std::vector<reco::TransientTrack> t_tks;
t_tks.clear();
t_tks.push_back( (*trkBuild).build(muon1.get()));
t_tks.push_back( (*trkBuild).build(muon2.get()));
TransientVertex dimu_vtx;
if(t_tks.size() > 1){
KalmanVertexFitter kvf(true);
dimu_vtx = kvf.vertex(t_tks);
}
if(dimu_vtx.isValid() && dimu_vtx.totalChiSquared() >= 0. && dimu_vtx.degreesOfFreedom() > 0){
//std::cout << "Normalized Qui2 do Vertice: \t" << dimu_vtx.totalChiSquared()/dimu_vtx.degreesOfFreedom() << std::endl;
vtxNormQui2[i] = dimu_vtx.totalChiSquared()/dimu_vtx.degreesOfFreedom();
//std::cout << "Normalized Qui2 do Vertice (z coordinate): \t" << dimu_vtx.position().z() << std::endl;
vtxZcoordinate[i] = dimu_vtx.position().z();
//std::cout << "Normalized Qui2 do Vertice (r distance): \t" << dimu_vtx.position().perp() << std::endl;
vtxRdistance[i] = dimu_vtx.position().perp();
//Dimuon Vertex x and y coordinate
double dimu_vtx_X,dimu_vtx_Y;
dimu_vtx_X = dimu_vtx.position().x();
dimu_vtx_Y = dimu_vtx.position().y();
//double dimu_vtx_rDist = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Power(dimu_vtx_X,2) + TMath::Power(dimu_vtx_Y,2));
//std::cout << "Normalized Qui2 do Vertice (r distance) NEW NEW : \t" << dimu_vtx_rDist << std::endl;
//r distance with respect to the beam spot
double bsx, bsy;
bsx = BSPosition.x();
bsy = BSPosition.y();
//std::cout << "BSPosition.x() = " << bsx << " BSPosition.y() = " << bsy << std::endl;
double rxy_vtx_bs;
rxy_vtx_bs = std::sqrt( (bsx-dimu_vtx_X)*(bsx-dimu_vtx_X) + (bsy-dimu_vtx_Y)*(bsy-dimu_vtx_Y) );
vtxRdistanceFromBS[i] = rxy_vtx_bs;
// important! evaluate momentum vectors AT THE VERTEX
TrajectoryStateClosestToPoint tag_TSCP = t_tks[0].trajectoryStateClosestToPoint(dimu_vtx.position());
TrajectoryStateClosestToPoint probe_TSCP = t_tks[1].trajectoryStateClosestToPoint(dimu_vtx.position());
GlobalVector tag_momentum = tag_TSCP.momentum();
GlobalVector probe_momentum = probe_TSCP.momentum();
//Tag pt
double tag_px = tag_momentum.x();
double tag_py = tag_momentum.y();
//std::cout << "tag px: " << tag_px << " tag py: " << tag_py << std::endl;
tagPtAtTheVtx[i] = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Power(tag_px,2) + TMath::Power(tag_py,2));
tagPtBefore[i] = mu1->pt();
//Probe pt
double probe_px = probe_momentum.x();
double probe_py = probe_momentum.y();
//std::cout << "probe px: " << probe_px << " probe py: " << probe_py << std::endl;
probePtAtTheVtx[i] = TMath::Sqrt(TMath::Power(probe_px,2) + TMath::Power(probe_py,2));
probePtBefore[i] = mu2->pt();
}else{
//std::cout << "Qui2 do Vertice ----- VERTEX IS NOT VALID!!!" << std::endl;
}
}
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, vtxNormQui2, "vtxNormQui2");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, vtxZcoordinate, "vtxZcoordinate");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, vtxRdistance, "vtxRdistance");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, vtxRdistanceFromBS, "vtxRdistanceFromBS");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, tagPtAtTheVtx, "tagPtAtTheVtx");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, probePtAtTheVtx, "probePtAtTheVtx");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, tagPtBefore, "tagPtBefore");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, probePtBefore, "probePtBefore");
...
// ------------ method fills 'descriptions' with the allowed parameters for the module ------------
void
DimuonVtxProducer::fillDescriptions(edm::ConfigurationDescriptions& descriptions) {
//The following says we do not know what parameters are allowed so do no validation
// Please change this to state exactly what you do use, even if it is no parameters
edm::ParameterSetDescription desc;
desc.setUnknown();
descriptions.addDefault(desc);
}
void
DimuonVtxProducer::writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const
{
using namespace edm;
using namespace std;
auto_ptr<ValueMap<float> > valMap(new ValueMap<float>());
edm::ValueMap<float>::Filler filler(*valMap);
filler.insert(handle, values.begin(), values.end());
filler.fill();
iEvent.put(valMap, label);
}
reco::TrackRef DimuonVtxProducer::mu_track(const reco::Muon & mu){
reco::TrackRef to_return;
if(mu.isStandAloneMuon()) to_return = mu.outerTrack();
if(mu.isTrackerMuon()) to_return = mu.innerTrack();
if(mu.isGlobalMuon()) to_return = mu.globalTrack();
return to_return;
}
See example
here
. This producer introduces these variables to the tree:
- χ2 of the vertex fit of the Tag and Probe pairs;
- z coordinate of the vertex;
- r = √(x2 + y2) vertex distance from the detector origin;
- r = √(x2 + y2) vertex distance from the beam spot;
- Δx and Δy of the vertex position between two muons;
- pT of Tag and Probe muons after the vertex fit (because some changes are expected after redefining the vertex);
- pT of Tag and Probe muons before the vertex fit (for comparison purposes).
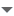
Two vertex distances (in the transverse plane) have been listed above, but only the vertex distance from the beam spot is the correct one. Simulated beam spot positions on MC events are different from what is found on events from real data. Then the vertex distance is not computed considering the center of the detector, but the with respect to the beam spot position. The vertex distance from Data events is very different than the distribution from MC events when considering the detector origin (figure on the left). On the other hand, when taking the beam spot into account, Data and MC agrees (figure on the right):

Variable: Collinearity
As described in the section 5.5 of
Analysis Note 12-422
,
"Cosmic ray muons traversing the detector near the IP in time with a collision event can be reconstructed as a pair of opposite-sign muons with dimuon invariant masses extending to quite high values. This background is suppressed by applying cuts on the muons' impact parameters and the 3D angle between muons, and by requiring the presence of a reconstructed primary vertex in the event".
and in section 3.2,
"To reduce the background from cosmic ray muons that are in-time with a collision event and pass the primary vertex and impact parameter cuts, we require that the three-dimensional angle between the two muons’ momenta be less than π - 0.02 rad".
Therefore,
collinearity is defined as the difference of π and the angle between muon tracks in the 3D space, and is implemented here using
ValueMap.
cd VetoCosmicMuonsProducer/
Include the following lines inside
BuildFile.xml
<use name="RecoMuon/MuonIdentification"/>
<use name="DataFormats/TrackReco"/>
Then, following this
example
, prepare the producer
src/VetoCosmicMuonsProducer.cc:
//my includes
#include "RecoMuon/MuonIdentification/interface/MuonCosmicsId.h"
#include "DataFormats/TrackReco/interface/Track.h"
#include "FWCore/Utilities/interface/InputTag.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/ValueMap.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/View.h"
#include "DataFormats/Candidate/interface/CompositeCandidate.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/Muon.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/MuonCocktails.h"
#include "TVector3.h"
...
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::InputTag src_;
/// Write a ValueMap<float> in the event
void writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const ;
...
// constructors and destructor
//
VetoCosmicMuonsProducer::VetoCosmicMuonsProducer(const edm::ParameterSet& iConfig) :
src_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("src"))
{
...
//now do what ever other initialization is needed
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("collinearity1");
...
// ------------ method called to produce the data ------------
void
VetoCosmicMuonsProducer::produce(edm::Event& iEvent, const edm::EventSetup& iSetup)
{
using namespace edm;
Handle<View<reco::Candidate> > src;
iEvent.getByLabel(src_, src);
size_t n = src->size();
std::vector<float> collinearity1(n,-999);
for(size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
const reco::Candidate & ci = (*src)[i];
if (ci.numberOfDaughters() != 2) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") <<
"DimuonVtxProducer should be used on composite candidates with two daughters, this one has " << ci.numberOfDaughters() << "\n";
const reco::Candidate &d1 = *ci.daughter(0), &d2 = *ci.daughter(1);
const reco::Muon *mu1 = dynamic_cast<const reco::Muon *>(&*d1.masterClone());
if (mu1 == 0) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") << "First daughter of candidate is not a ShallowClone of a reco::Muon\n";
reco::Muon::MuonTrackTypePair tuneP1 = muon::tevOptimized(*mu1, 200, 40., 17., 0.25);
const reco::Muon *mu2 = dynamic_cast<const reco::Muon *>(&*d2.masterClone());
if (mu2 == 0) throw cms::Exception("CorruptData") << "Second daughter of candidate is not a ShallowClone of a reco::Muon\n";
reco::Muon::MuonTrackTypePair tuneP2 = muon::tevOptimized(*mu2, 200, 40., 17., 0.25);
float tag_pX = tuneP1.first->px();
float tag_pY = tuneP1.first->py();
float tag_pZ = tuneP1.first->pz();
TVector3 tag_Pxyz(tag_pX,tag_pY,tag_pZ);
float probe_pX = tuneP2.first->px();
float probe_pY = tuneP2.first->py();
float probe_pZ = tuneP2.first->pz();
TVector3 probe_Pxyz(probe_pX,probe_pY,probe_pZ);
//Angle between two vectors
collinearity1[i] = tag_Pxyz.Angle(probe_Pxyz);
}
writeValueMap(iEvent, src, collinearity1, "collinearity1");
...
// ------------ method fills 'descriptions' with the allowed parameters for the module ------------
void
VetoCosmicMuonsProducer::fillDescriptions(edm::ConfigurationDescriptions& descriptions) {
//The following says we do not know what parameters are allowed so do no validation
// Please change this to state exactly what you do use, even if it is no parameters
edm::ParameterSetDescription desc;
desc.setUnknown();
descriptions.addDefault(desc);
}
void
VetoCosmicMuonsProducer::writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const
{
using namespace edm;
using namespace std;
auto_ptr<ValueMap<float> > valMap(new ValueMap<float>());
edm::ValueMap<float>::Filler filler(*valMap);
filler.insert(handle, values.begin(), values.end());
filler.fill();
iEvent.put(valMap, label);
}
Variable: GenParticles
Let's now add variables related to the
GenParticles (which are
GenMuon of both negative and positive signal). They are: p
T, η, φ and mass(μ
1,μ
2).
cd GenPVariablesProducer/
Include these lines inside
BuildFile.xml
<use name="FWCore/Utilities"/>
<use name="DataFormats/Common"/>
<use name="DataFormats/Candidate"/>
<use name="DataFormats/MuonReco"/>
<use name="DataFormats/HepMCCandidate"/>
Now fill
src/GenPVariablesProducer.cc producer with these peaces of code
//my includes
#include "FWCore/Utilities/interface/InputTag.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/ValueMap.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/View.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/Muon.h"
#include "DataFormats/HepMCCandidate/interface/GenParticle.h"
...
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::InputTag src_;
edm::InputTag obj_;
/// Write a ValueMap<float> in the event
void writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const ;
...
// constructors and destructor
//
GenPVariablesProducer::GenPVariablesProducer(const edm::ParameterSet& iConfig) :
src_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("src")),
obj_(iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>("obj"))
{
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuPluspt");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuPluseta");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuPlusphi");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuMinuspt");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuMinuseta");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vMuMinusphi");
produces<edm::ValueMap<float> >("vDimuMass");
...
// ------------ method called to produce the data ------------
void
GenPVariablesProducer::produce(edm::Event& iEvent, const edm::EventSetup& iSetup)
{
using namespace edm;
Handle<View<reco::Candidate> > src;
iEvent.getByLabel(src_, src);
Handle<std::vector<reco::GenParticle> > objects;
iEvent.getByLabel(obj_, objects);
size_t n = src->size();
float MuPlus_pt(-999.0),MuPlus_eta(-999.0),MuPlus_phi(-999.0),MuMinus_pt(-999.0),MuMinus_eta(-999.0),MuMinus_phi(-999.0),DimuMass(-999.0);
int nMuPlus=0;
int nMuMinus=0;
const reco::GenParticle * MPlus = 0;
const reco::GenParticle * MMinus = 0;
for(size_t ngenPart=0; ngenPart<objects->size(); ngenPart++){
const reco::GenParticle & genPart = (*objects)[ngenPart];
if(genPart.pdgId()==13 && genPart.status()==1){
nMuMinus++;
MMinus = &genPart;
}
if(genPart.pdgId()==-13 && genPart.status()==1){
nMuPlus++;
MPlus = &genPart;
}
}
if( (nMuMinus==1) && (nMuPlus==1) ){
MuPlus_pt = MPlus->pt();
MuPlus_eta = MPlus->eta();
MuPlus_phi = MPlus->phi();
MuMinus_pt = MMinus->pt();
MuMinus_eta = MMinus->eta();
MuMinus_phi = MMinus->phi();
DimuMass = (MPlus->p4() + MMinus->p4()).mass();
}
std::vector<float> vMuPluspt(n,MuPlus_pt),vMuPluseta(n,MuPlus_eta),vMuPlusphi(n,MuPlus_phi),vMuMinuspt(n,MuMinus_pt),vMuMinuseta(n,MuMinus_eta),vMuMinusphi(n,MuMinus_phi),vDimuMass(n,DimuMass);
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuPluspt , "vMuPluspt");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuPluseta , "vMuPluseta");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuPlusphi , "vMuPlusphi");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuMinuspt , "vMuMinuspt");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuMinuseta, "vMuMinuseta");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vMuMinusphi , "vMuMinusphi");
writeValueMap(iEvent, src,vDimuMass , "vDimuMass");
...
// ------------ method fills 'descriptions' with the allowed parameters for the module ------------
void
GenPVariablesProducer::fillDescriptions(edm::ConfigurationDescriptions& descriptions) {
//The following says we do not know what parameters are allowed so do no validation
// Please change this to state exactly what you do use, even if it is no parameters
edm::ParameterSetDescription desc;
desc.setUnknown();
descriptions.addDefault(desc);
}
void
GenPVariablesProducer::writeValueMap(edm::Event &iEvent,
const edm::Handle<edm::View<reco::Candidate> > & handle,
const std::vector<float> & values,
const std::string & label) const
{
using namespace edm;
using namespace std;
auto_ptr<ValueMap<float> > valMap(new ValueMap<float>());
edm::ValueMap<float>::Filler filler(*valMap);
filler.insert(handle, values.begin(), values.end());
filler.fill();
iEvent.put(valMap, label);
}
See example
here
.
Variable: NewTuneP
To add variables with information from
NewTuneP:
UserFloat will be used instead of
ValueMap. For this different procedure, a new collection of muons are created before Tag and Probe muons themselves being create.
CAUTION: it is necessary to change several parts of
tp_from_aod_Data/MC.py.
cd NewTunePMuonsProducer/
Include these lines in
BuildFile.xml, as
<use name="DataFormats/MuonReco"/>
<use name="DataFormats/PatCandidates"/>
<use name="DataFormats/VertexReco"/>
Include these lines in
src/NewTunePMuonsProducer.cc:
//my includes
#include "FWCore/Utilities/interface/InputTag.h"
#include "DataFormats/Common/interface/Handle.h"
#include "DataFormats/PatCandidates/interface/Muon.h"
#include "DataFormats/VertexReco/interface/Vertex.h"
#include "DataFormats/VertexReco/interface/VertexFwd.h"
#include "DataFormats/MuonReco/interface/MuonSelectors.h"
#include "FWCore/MessageLogger/interface/MessageLogger.h"
#include <vector>
...
// ----------member data ---------------------------
edm::InputTag src_;
edm::InputTag vtx_;
...
// constructors and destructor
//
NewTunePMuonsProducer::NewTunePMuonsProducer(const edm::ParameterSet& iConfig) :
src_( iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>( "src" ) ),
vtx_( iConfig.getParameter<edm::InputTag>( "vtx" ) )
{
...
//now do what ever other initialization is needed
produces<std::vector<pat::Muon> >();
...
// ------------ method called to produce the data ------------
void
NewTunePMuonsProducer::produce(edm::Event& iEvent, const edm::EventSetup& iSetup)
{
using namespace edm;
Handle<reco::VertexCollection> recVtxs;
iEvent.getByLabel(vtx_, recVtxs);
// From CMSSW/Validation/RecoMuon/src/RecoMuonValidator.cc
// Look for the Primary Vertex (and use the BeamSpot instead, if you can't find it):
reco::Vertex::Point posVtx;
reco::Vertex::Error errVtx;
//edm::Handle<reco::VertexCollection> recVtxs;
//event.getByLabel(primvertexLabel_,recVtxs);
unsigned int theIndexOfThePrimaryVertex = 999.;
for (unsigned int ind=0; ind<recVtxs->size(); ++ind) {
if ( (*recVtxs)[ind].isValid() && !((*recVtxs)[ind].isFake()) ) {
theIndexOfThePrimaryVertex = ind;
break;
}
}
if (theIndexOfThePrimaryVertex<100) {
posVtx = ((*recVtxs)[theIndexOfThePrimaryVertex]).position();
errVtx = ((*recVtxs)[theIndexOfThePrimaryVertex]).error();
}
else {
LogInfo("RecoMuonValidator") << "reco::PrimaryVertex not found, use BeamSpot position instead\n";
//edm::Handle<reco::BeamSpot> recoBeamSpotHandle;
//event.getByLabel(beamspotLabel_,recoBeamSpotHandle);
Handle<reco::BeamSpot> recoBeamSpotHandle;
iEvent.getByLabel("offlineBeamSpot",recoBeamSpotHandle);
reco::BeamSpot bs = *recoBeamSpotHandle;
posVtx = bs.position();
errVtx(0,0) = bs.BeamWidthX();
errVtx(1,1) = bs.BeamWidthY();
errVtx(2,2) = bs.sigmaZ();
}
const reco::Vertex thePrimaryVertex(posVtx,errVtx);
Handle< std::vector<pat::Muon> > muons;
iEvent.getByLabel(src_,muons);
std::auto_ptr< std::vector<pat::Muon> > muonColl( new std::vector<pat::Muon> (*muons) );
for(unsigned int i = 0; i< muonColl->size();++i){
pat::Muon & m = (*muonColl)[i];
//redefined track
reco::TrackRef cktTrack;
cktTrack = muon::improvedMuonBestTrack(m, muon::improvedTuneP);
//pt, ptRelError, eta and phi
float NewTunePpt = cktTrack->pt();
float NewTunePptRelError = cktTrack->ptError()/cktTrack->pt();
float NewTunePeta = cktTrack->eta();
float NewTunePphi = cktTrack->phi();
//is High Pt muon (using the newTuneP definition)
float isNewHPTmuonGlobal = 0.0;
if(muon::isHighPtMuon(m,thePrimaryVertex))isNewHPTmuonGlobal = 1.0;
m.addUserFloat("IsNewHPTmuonGlobal", isNewHPTmuonGlobal);
m.addUserFloat("NEWTUNEPpt", NewTunePpt);
m.addUserFloat("NEWTUNEPptRelError",NewTunePptRelError);
m.addUserFloat("NEWTUNEPeta",NewTunePeta);
m.addUserFloat("NEWTUNEPphi",NewTunePphi);
}
iEvent.put(muonColl);
See example
here
.
Setting Up Config Files
Complete

It is needed to "import" the modules. There is a dedicated module for these purposes in the MuonPOG T&P package. Open the file
MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/python/common_modules_cff.py and add this peaces of code to import the modules and put the collections of interest:
import MuonAnalysis.METProducer.metproducer_cfi
MetModule = MuonAnalysis.METProducer.metproducer_cfi.demo.clone(
probes = cms.InputTag("tagMuons"),
objects = cms.InputTag("pfMet"),
)
DimuonVtxModule = cms.EDProducer("DimuonVtxProducer",
src = cms.InputTag("tpPairs"),
)
patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons = cms.EDProducer("NewTunePMuonsProducer",
src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTrigger"),
vtx = cms.InputTag("offlinePrimaryVertices"),
)
VetoCosmicMuonsModule = cms.EDProducer("VetoCosmicMuonsProducer",
src = cms.InputTag("tpPairs"),
)
GenPVariablesModule = cms.EDProducer("GenPVariablesProducer",
src = cms.InputTag("tpPairs"),
obj = cms.InputTag("genParticles"),
)

is example of
common_modules_cff.py.
To implement the
ΔpT/pT (from inner track fit) for Tag muon, open file
MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/python/common_variables_cff.py and under
TrackQualityVariables = cms.PSet add this selector string:
innertkSigmaPtOverPt = cms.string("? innerTrack.isNull ? -1 : innerTrack.ptError/innerTrack.pt"),
See an example of config file
common_variables_cff.py here
.
A last step to add variables to trees is setting up the main config file
tp_from_aod_MC.py as the following:
...
process.tagMuons = cms.EDFilter("PATMuonSelector",
## src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTrigger"),
src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons"),
cut = cms.string("pt > 15 && "+MuonIDFlags.Tight2012.value()+
" && !triggerObjectMatchesByCollection('hltL3MuonCandidates').empty()"+
" && pfIsolationR04().sumChargedHadronPt/pt < 0.2"),
)
...
process.probeMuons = cms.EDFilter("PATMuonSelector",
## src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTrigger"),
src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons"),
#cut = cms.string("track.isNonnull"), # no real cut now
cut = cms.string("track.isNonnull && pt > 15"), # no real cut now
)
...
process.tpPairs = cms.EDProducer("CandViewShallowCloneCombiner",
#cut = cms.string('60 < mass < 140 && abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
#cut = cms.string('60 < mass && abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
cut = cms.string('abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
#decay = cms.string('tagMuons@+ probeMuons@-'),
decay = cms.string('tagMuons probeMuons'),
checkCharge = cms.bool(False)
)
...
# probe variables: all useful ones
variables = cms.PSet(
AllVariables,
ExtraIsolationVariables,
MVAIsoVariablesPlain,
isoTrk03Abs = cms.InputTag("probeMuonsIsoValueMaps","probeMuonsIsoFromDepsTk"),
isoTrk03Rel = cms.InputTag("probeMuonsIsoValueMaps","probeMuonsRelIsoFromDepsTk"),
dxyBS = cms.InputTag("muonDxyPVdzmin","dxyBS"),
dxyPVdzmin = cms.InputTag("muonDxyPVdzmin","dxyPVdzmin"),
dzPV = cms.InputTag("muonDxyPVdzmin","dzPV"),
radialIso = cms.InputTag("radialIso"),
nSplitTk = cms.InputTag("splitTrackTagger"),
###New Variables by Cesar and Angelo
IsNewHPTmuon = cms.string("userFloat('IsNewHPTmuonGlobal')"),
NewTuneP_pt = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPpt')"),
NewTuneP_ptRelError = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPptRelError')"),
NewTuneP_eta = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPeta')"),
NewTuneP_phi = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPphi')"),
),
...
tagVariables = cms.PSet(
TriggerVariables,
MVAIsoVariablesPlainTag,
pt = cms.string("pt"),
eta = cms.string("eta"),
phi = cms.string("phi"),
nVertices = cms.InputTag("nverticesModule"),
combRelIso = cms.string("(isolationR03.emEt + isolationR03.hadEt + isolationR03.sumPt)/pt"),
chargedHadIso04 = cms.string("pfIsolationR04().sumChargedHadronPt"),
neutralHadIso04 = cms.string("pfIsolationR04().sumNeutralHadronEt"),
photonIso04 = cms.string("pfIsolationR04().sumPhotonEt"),
dzPV = cms.InputTag("muonDxyPVdzminTags","dzPV"),
###New Variables by Cesar and Angelo
MET = cms.InputTag("MetModule"),
combRelIsoPF04dBeta = IsolationVariables.combRelIsoPF04dBeta,
IsNewHPTmuon = cms.string("userFloat('IsNewHPTmuonGlobal')"),
NewTuneP_pt = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPpt')"),
NewTuneP_ptRelError = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPptRelError')"),
NewTuneP_eta = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPeta')"),
NewTuneP_phi = cms.string("userFloat('NEWTUNEPphi')"),
innertrackPtRelError = TrackQualityVariables.innertkSigmaPtOverPt,
charge = cms.string("charge"),
),
...
pairVariables = cms.PSet(
nJets30 = cms.InputTag("njets30Module"),
dz = cms.string("daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz"),
pt = cms.string("pt"),
rapidity = cms.string("rapidity"),
deltaR = cms.string("deltaR(daughter(0).eta, daughter(0).phi, daughter(1).eta, daughter(1).phi)"),
probeMultiplicity = cms.InputTag("probeMultiplicity"),
## New TuneP variables
newTuneP_probe_pt = cms.InputTag("newTunePVals", "pt"),
newTuneP_probe_sigmaPtOverPt = cms.InputTag("newTunePVals", "ptRelError"),
newTuneP_probe_trackType = cms.InputTag("newTunePVals", "trackType"),
newTuneP_mass = cms.InputTag("newTunePVals", "mass"),
###New Variables by Cesar and Angelo
DimuonVtxFitNormQui2 = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "vtxNormQui2"),
DimuonVtxZcoordinate = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "vtxZcoordinate"),
DimuonVtxRdistance = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "vtxRdistance"),
DimuonVtxTagPtAtTheVtx = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "tagPtAtTheVtx"),
DimuonVtxProbePtAtTheVtx = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "probePtAtTheVtx"),
DimuonVtxTagPtBefore = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "tagPtBefore"),
DimuonVtxProbePtBefore = cms.InputTag("DimuonVtxModule", "probePtBefore"),
collinearity1 = cms.InputTag("VetoCosmicMuonsModule", "collinearity1"),
GenPVar_MuPlusPt = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuPluspt"),
GenPVar_MuPlusEta = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuPluseta"),
GenPVar_MuPlusPhi = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuPlusphi"),
GenPVar_MuMinusPt = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuMinuspt"),
GenPVar_MuMinusEta = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuMinuseta"),
GenPVar_MuMinusPhi = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vMuMinusphi"),
GenPVar_DimuMass = cms.InputTag("GenPVariablesModule", "vDimuMass"),
),
...
process.tnpSimpleSequence = cms.Sequence(
process.tagMuons * process.tagMuonsMCMatch +
process.oneTag +
process.probeMuons * process.probeMuonsMCMatch +
process.tpPairs +
process.onePair +
process.nverticesModule +
process.njets30Module +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.MetModule +
process.DimuonVtxModule +
process.VetoCosmicMuonsModule +
process.GenPVariablesModule +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.extraProbeVariablesSeq +
process.probeMultiplicity +
process.bestPairByZMass +
process.newTunePVals +
process.muonDxyPVdzminTags +
process.tpTree
)
process.tagAndProbe = cms.Path(
process.fastFilter +
process.mergedMuons *
process.patMuonsWithTriggerSequence +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.tnpSimpleSequence
)
...
process.tagAndProbeSta = cms.Path(
process.fastFilter +
process.muonsSta +
process.patMuonsWithTriggerSequenceSta +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.tnpSimpleSequenceSta
)
...
process.fakeRateJetPlusProbe = cms.Path(
process.fastFilter +
process.mergedMuons * process.patMuonsWithTriggerSequence +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.tagMuons + process.probeMuons + process.extraProbeVariablesSeq +
process.jetPlusProbeSequence +
process.fakeRateJetPlusProbeTree
)
process.fakeRateWPlusProbe = cms.Path(
process.fastFilter +
process.mergedMuons * process.patMuonsWithTriggerSequence +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.tagMuons + process.probeMuons + process.extraProbeVariablesSeq +
process.wPlusProbeSequence +
process.fakeRateWPlusProbeTree
)
process.fakeRateZPlusProbe = cms.Path(
process.fastFilter +
process.mergedMuons * process.patMuonsWithTriggerSequence +
### Cesar and Angelo Begin
process.patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons +
### Cesar and Angelo End
process.tagMuons + process.probeMuons + process.extraProbeVariablesSeq +
process.zPlusProbeSequence +
process.fakeRateZPlusProbeTree
)
See example
here
.
Please, click bellow to take notes about a few instructions and explanations:
- Configuration for
tp_from_aod_Data.py is similar, but without information from GenParticles. See here an example of config file to produce Data trees.
an example of config file to produce Data trees.
- Config file for Data has a global tag different than the default:
if "CMSSW_5_3_" in os.environ['CMSSW_VERSION']:
# process.GlobalTag.globaltag = cms.string('GR_P_V42_AN2::All')
process.GlobalTag.globaltag = cms.string('FT_53_V21_AN4::All')
- For this study is required that both Data and MC config files has a "SingleMu" trigger:
## SELECT WHAT DATASET YOU'RE RUNNING ON
TRIGGER="SingleMu"
#TRIGGER="DoubleMu"
- Since conveners of MuonPOG are not sure about the selection to be applied on the mass of the T&P pairs, no cut is done. And to avoid producing two sets of trees (one with opposite-charge muons and other with same-charge muons), there is no muon charge requirement:
process.tpPairs = cms.EDProducer("CandViewShallowCloneCombiner",
#cut = cms.string('60 < mass < 140 && abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
#cut = cms.string('60 < mass && abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
cut = cms.string('abs(daughter(0).vz - daughter(1).vz) < 4'),
#decay = cms.string('tagMuons@+ probeMuons@-'),
decay = cms.string('tagMuons probeMuons'),
checkCharge = cms.bool(False)
)
- Make sure that the flag
MVAIsoVariablesPlainTag is also there (as indicated above). It is important for PFCombined.
- ΔpT/pT has been add into
tp_from_aod_MC.py and tp_from_aod_Data.py though
tagVariables = cms.PSet(
...
InnerTkSigmaPtOverPt = TrackQualityVariables.innertkSigmaPtOverPt,
...
charge = cms.string("charge"),
),
- The charge of muons is also included in
tagVariables so Tag muons can also keep information about charge.
- The Probe muon is required to have pT > 15 GeV to reduce the size of trees
process.probeMuons = cms.EDFilter("PATMuonSelector",
## src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTrigger"),
src = cms.InputTag("patMuonsWithTriggerOurMuons"),
#cut = cms.string("track.isNonnull"), # no real cut now
cut = cms.string("track.isNonnull && pt > 15"), # no real cut now
)
- PFCombined isolation with beta correction has been added directly into
tp_from_aod_MC.py and tp_from_aod_Data.py because this variable is already implemented in MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/python/common_variables_cff.py under IsolationVariables = cms.PSet in this way
combRelIsoPF04dBeta = cms.string("(pfIsolationR04().sumChargedHadronPt + max(pfIsolationR04().sumNeutralHadronEt + pfIsolationR04().sumPhotonEt - pfIsolationR04().sumPUPt/2,0.0))/pt"),
Production of Trees
Complete

Following sub-sections contain:
- information about sets of Data and MC events used in this task;
- scripts and instructions to create trees via CRAB;
- scripts and instructions to merge ROOT files;
- scripts and instructions to correct MC events via reweighting of vertex multiplicity;
- and information about the new trees.
Datasets for Data and MC Samples
In a first moment, only 7 fb
-1 of integrated luminosity (corresponding to the RunC data taking period) is analyzed to make the first cross checks and to test the method of computing efficiencies out of the Z mass window. Later on, Data trees with a total of 19.7 fb
-1 of integrated luminosity (w.r.t. 2012 period) will be produced.
The same list of MC samples of the
Analysis Note 12-422
(section 2.2, table 3) is used to produce the trees. For the meantime, only Drell-Yan→μμ samples of different m(μ
1, μ
2) windows have been used, while the other SM processes are left to when DY samples were well understand. That is, when:
- having only one pair of T&P muons per event;
- the Tag and Probe are different muons;
- making sure the T&P muons come from the same vertex.
Here are the Data and MC samples used to produce the trees. Second and third rows correspond to the same sample, but the third one has much more events. The last row corresponds to a sample of Drell-Yan+Jets which is used as a control sample, and is not listed in Analysis Note above.
| Process |
Invariant_Mass_Window |
Cross_Section_x_Loop(pb) |
Number_of_Events |
Data Set |
| Data-RunC |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
--- |
87683348 |
/SingleMu/Run2012C-22Jan2013-v1/AOD |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
1915 (NNLO) |
3293740 |
/DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
1915 (NNLO) |
48819386 |
/DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_v2_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 120 GeV |
12.17 (NLO x 1.024) |
99984 |
/DYToMuMu_M-120_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 200 GeV |
1.520 (NLO x 1.024) |
99990 |
/DYToMuMu_M-200_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 500 GeV |
0.04519 (NLO x 1.024) |
99992 |
/DYToMuMu_M-500_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 800 GeV |
0.005620 (NLO x 1.024) |
99984 |
/DYToMuMu_M-800_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1000 GeV |
0.001838 (NLO x 1.024) |
99989 |
/DYToMuMu_M-1000_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1500 GeV |
1.745E-4 (NLO x 1.024) |
99992 |
/DYToMuMu_M-1500_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 2000 GeV |
2.260E-5 (NLO x 1.024) |
99974 |
/DYToMuMu_M-2000_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1/AODSIM |
| DY→τ+τ- |
m(τ+, τ-) > 20 GeV |
1915 (NNLO) |
3295238 |
/DYToTauTau_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| ttbar |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
234 (NNLO) |
21675970 |
/TT_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v2/AODSIM |
| tW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
11.1 (NNLO) |
497658 |
/T_tW-channel-DR_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| tbarW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
11.1 (NNLO) |
493460 |
/Tbar_tW-channel-DR_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| WW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
54.8 (NLO) |
10000431 |
/WW_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| WZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
33.2 (NLO) |
10000283 |
/WZ_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| ZZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
17.6 (NLO) |
9799908 |
/ZZ_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| W+Jets |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
36257 (NNLO) |
18393090 |
/WJetsToLNu_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph-tarball/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
| Inclusive QCD |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
3.64E8 x 3.7E-4 (LO) |
21484602 |
/QCD_Pt_20_MuEnrichedPt_15_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v3/AODSIM |
| DY+Jets→ll |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
--- |
30459503 |
/DYJetsToLL_M-50_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph-tarball/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM |
Submitting Jobs to CRAB
Before submitting jobs to CRAB, setup the Grid with
cd ~/.
source /afs/cern.ch/cms/LCG/LCG-2/UI/cms_ui_env.sh
cd -
cmsenv
source /afs/cern.ch/cms/ccs/wm/scripts/Crab/crab.sh
voms-proxy-init
This is the configuration file (
crab_DATA.cfg) to produce Data tree
[CMSSW]
number_of_jobs = 500
total_number_of_lumis = -1
pset = tp_from_aod_Data.py
datasetpath = /SingleMu/Run2012C-22Jan2013-v1/AOD
output_file = tnpZ_HighMassDimuon.root
[USER]
ui_working_dir = SingleMuRun2012C_22Jan2013_v1_Dec_15_2013
return_data = 0
email = your.username@cern.ch
copy_data = 1
storage_element = T2_BR_SPRACE
user_remote_dir = SingleMuRun2012C_22Jan2013_v1_Dec_15_2013
[CRAB]
scheduler = remoteGlidein
jobtype = cmssw
use_server = 0
See example
here
. Modify according your needs.
This is the configuration file (
crab_MC.cfg) to produce MC trees
[CMSSW]
total_number_of_events = 3293740
number_of_jobs = 50
pset = tp_from_aod_MC.py
datasetpath = /DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6/Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1/AODSIM
[USER]
return_data = 0
email = your.username@cern.ch
ui_working_dir = DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1
copy_data = 1
storage_element = T2_BR_SPRACE
user_remote_dir = DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1
[CRAB]
scheduler = remoteGlidein
jobtype = cmssw
use_server = 0
[GRID]
se_white_list = T2_BR_SPRACE
See example
here
. Both config files for CRAB are set to send the output files to
T2_SPRACE.
These are the steps to submit the jobs:
- prepare the files to be submitted:
crab -create -cfg crab_DATA.cfg
It will generate a file with the same name as that given in ui_working_dir inside the config file.
- submit the jobs:
crab -submit -c <crab directory>
- check status of jobs:
crab -status -c <crab directory>
In case of desiring to see only a status report, type crab -status short,color -c <crab directory>
- get information about jobs when they have finished:
crab -getoutput [range] -c <crab directory>
where [range] is the range of jobs. For example, crab -getoutput 1,23,52-61 -c <crab directory>
which will get information of jobs 1, 23 and from 52 to 61.
- get report:
crab -report -c <crab directory>
This command outputs on the screen a report about the total number of events, files and jobs analyzed through CRAB, and create the file <crab directory>/res/lumiSummary.json
containing the range of block numbers, in case of Data events. It is useful to check if the final number of events and jobs are the expected ones.
When running over Data events, it is important to get the total integrated luminosity correspondent to that data set. It is need to setup the luminosity tools. For further information on how to set these tools, look at
here
. Then when the jobs were terminated:
- get report to generate the json file (as explained above):
crab -report -c <crab directory>
- compare this json file with the golden json file:
compareJSON.py --and <crab directory>/res/lumiSummary.json /afs/cern.ch/cms/CAF/CMSCOMM/COMM_DQM/certification/Collisions12/8TeV/Reprocessing/Cert_190456-208686_8TeV_22Jan2013ReReco_Collisions12_JSON.txt jsonAND.json
where jsonAND.json will be used to get the processed luminosity.
- compute luminosity:
pixelLumiCalc.py -i jsonAND.json overview
The total integrated luminosity for the correspondent data set is written in the last column of the last table.
Output files from CRAB were place in the
T2_SPRACE storage:
srm://osg-se.sprace.org.br:8443/srm/managerv2?SFN=/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_Dec_23_2013/
Merging Files
Beforing starting to merge files, type
cmsenv to avoid problems with
hadd command. Since lots of root files are produced via CRAB (from tens to hundreds), it is useful to merge this files. Create a list of them (which are located at
T2_SPRACE storage) using the command
source /home/assantos/scripts/create_list_of_StorageFiles.sh hadd /pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/bla/bla/bla/
where bla/bla/bla is the rest of the path where the ROOT files are placed in. Such command create a list called
lll.txt. Then type
mv lll.txt file
To merge the ROOT files, run the command
source /home/assantos/scripts/haddScript.sh file
If the list of files is too big, this step may get stuck, needing to split the list
lll.txt in two or more file lists.
Here are the paths where ROOT trees of Data, DY→μμ and other SM samples are located at the ACCESS.
| Process |
Invariant_Mass_Window |
Number_of_Events |
Data Set Path at ACCESS |
| Data-RunC |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
73100236 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_SingleMuRun2012C_22Jan2013_v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
4817072 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
71411027 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_v2_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7A-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 120 GeV |
265550 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-120_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 200 GeV |
309663 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-200_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 500 GeV |
379473 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-500_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 800 GeV |
408182 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-800_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1000 GeV |
419382 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-1000_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1500 GeV |
436012 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-1500_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 2000 GeV |
441181 |
/home/assantos/MuonPOG/TagAndProbe/Task_01/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/datasets/Dec_23_2013/tnpZ_DYToMuMu_M-2000_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_Summer12_DR53X-PU_S10_START53_V7C1-v1.root |
| DY→ττ |
m(τ+, τ-) > 0 GeV |
222238 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_DYToTauTau_M-20_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-pythia6_V1_12122013.root |
| ttbar |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
11837860 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_TT_CT10_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| tW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
234414 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_T_tW-channel-DR_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| tbarW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
227851 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_Tbar_tW-channel-DR_TuneZ2star_8TeV-powheg-tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| WW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2643186 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_WW_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| WZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2511807 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_WZ_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| ZZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2592869 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_ZZ_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_tauola_V1_12122013.root |
| W+Jets |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
4117043 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_WJetsToLNu_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph-tarball_V1_12122013.root |
| Inclusive-QCD |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
5213103 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_QCD_Pt_20_MuEnrichedPt_15_TuneZ2star_8TeV_pythia6_V1_12122013.root |
| DY+Jets→ll |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
23611226 |
/home/bernardes/TnP_HighMassDimuonEff/CMSSW_5_3_10/src/MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/Trees_15122013/tnpZ_DYJetsToLL_M-50_TuneZ2Star_8TeV-madgraph_V1_12122013.root |
In case of needing to delete ROOT files saved on the storage:
- Create a list of those files. Suppose the files are inside the directory
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/bla/bla/bla/, then type:
source /home/assantos/scripts/create_list_of_StorageFiles.sh del /pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/bla/bla/bla/
It will create a list of files called
lll.txt.
xargs srmrm < lll.txt
Correction through Vertex Multiplicity
The MC samples have to be reweighted concerning the vertex multiplicity from Data events using the macro
MuonAnalysis/TagAndProbe/test/zmumu/addNVtxWeight.cxx. The macro
addNVtxWeight.cxx compares the vertex multiplicity distribution from Data with that one from a MC sample. After normalizing these distributions, differences from their shapes are taking into account to create a variable called
weight inside the new MC ROOT file. This step has to be done for each MC sample through the following command:
root -b -l -q <MC ROOT sample> <Data ROOT sample> addNVtxWeight.cxx+
It will create a
.png file showing distributions of vertex multiplicity of the Data and MC samples used, as well as the correspondent new MC ROOT file containing that additional variable
weight, which carries the weights to be applied later on to the events of the corresponding MC sample. Here is an example of the
.png file (figure on the left) and of the variable
weight (right) when comparing Data-RunC with MC DY→μμ [mass(μ
1, μ
2) > 20 GeV]:


These table shows the ROOT file paths of Data and MC samples (MC files with the variable
weight).
| Process |
Invariant_Mass_Window |
Number_of_Events |
Data Set Path in the Storage of T2_SPRACE |
| Data-RunC |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
73100236 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_SingleMuRun2012C_22Jan2013_v1.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
4817072 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_20_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 20 GeV |
71411027 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_20_withNVtxWeights_v2.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 120 GeV |
265550 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_120_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 200 GeV |
309663 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_200_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 500 GeV |
379473 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_200_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 800 GeV |
408182 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_800_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1000 GeV |
419382 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_1000_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 1500 GeV |
436012 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_1500_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→μμ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 2000 GeV |
441181 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_M_2000_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY→ττ |
m(τ+, τ-) > 0 GeV |
222238 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/DYToTauTau_M_20_withNVtxWeights.root |
| ttbar |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
11837860 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/ttbar_withNVtxWeights.root |
| tW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
234414 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/T_tW_withNVtxWeights.root |
| tbarW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
227851 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/Tbar_tW_withNVtxWeights.root |
| WW |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2643186 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/WW_withNVtxWeights.root |
| WZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2511807 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/WZ_withNVtxWeights.root |
| ZZ |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
2592869 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/ZZ_withNVtxWeights.root |
| W+Jets |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
4117043 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/WJetsToLNu_withNVtxWeights.root |
| Inclusive-QCD |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
5213103 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/QCD_Pt_20_MuEnrichedPt_15_withNVtxWeights.root |
| DY+Jets→ll |
m(μ1, μ2) > 0 GeV |
23611226 |
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithVertexReweighting_Dec_26_2013/tnpZ_DYJetsToLL_M_50_withNVtxWeights.root |
Bellow, figure on the left (right) shows the vertex multiplicity distribution from Data and MC samples before (after) apply the reweighting concerning the numbers of vertices. No extra selection is applied to Data and MC events.


Cross Checks Comparing Data and MC Distributions
Complete

After vertex reweighting, following sub-sections describe:
- how to use the ROOT files above as input files for scripts which creates several plots comparing Data and MC distributions;
- what selections are important to be applied to the pairs of T&P muons;
- how to clean up events to have the best choice of T&P muon pairs.
Macro Files
A macro file in
C++ has been written to produce plots comparing Data and MC distributions:
- Setting_Variables.h
 : Users have to apply all necessary changings into this macro. All lines were commented as better as possible.
: Users have to apply all necessary changings into this macro. All lines were commented as better as possible.
- TagAndProbe_stacks_V12.cpp
 : No need to modify this file. This macro will read all settings defined into
: No need to modify this file. This macro will read all settings defined into Setting_Variables.h and create the distributions.
To run these macros, just type (into either
ACCESS or
lxplus5):
root -b -l -q TagAndProbe _stacks_V12.cpp
NOTE: It is recommend to run these macros from ACCESS (will take ~ 30 minuntes). If running from lxplus5, it may take a whole day. Other solution has been tested to speed up this process as, for example, submitting scripts to Condor.
To run via Condor, additional macro files will be required, and file
Setting_Variables.h will no longer be need. Different than the method above, where all plots are produced in sequence through the same macro file, now each plot is created in parallel. Jobs are submitted to
Condor, and each plot is created in each job. Here are the scripts and macro files:
- Common_Settings.py
 : the script will ask user for providing a directory name which will be created to receive all plots from Condor. In the first part of the code, user can apply all necessary settings to create the plots. The rest of the file takes care of creating a
: the script will ask user for providing a directory name which will be created to receive all plots from Condor. In the first part of the code, user can apply all necessary settings to create the plots. The rest of the file takes care of creating a C++ header for each job. In the end, the script submit_TagAndProbe_to_condor.sh will be called to submit jobs to Condor, parallelizing the plots production.
- submit_TagAndProbe_to_condor.sh
 : will create a directory called "Processing" and copy the
: will create a directory called "Processing" and copy the C++ files into it. Then it will submit jobs to Condor.
- TagAndProbe_for_condor.submit
 : contains all settings used to run jobs on Condor. An specific flag (
: contains all settings used to run jobs on Condor. An specific flag (Requirements = Memory > 16*1024=) is used to require nodes with the highest memory because input ROOT files sum a total of 65 GB.
- TagAndProbe.sh
 : this script is sent to the nodes, setting up the
: this script is sent to the nodes, setting up the CMSSW environment and running C++ macro via ROOT.
- TagAndProbe_stacks_V12.cpp
 : this is the same macro files as mentioned above.
: this is the same macro files as mentioned above.
Thus, to submit jobs from
ACCESS to
Condor, setup the Grid
voms-proxy-init --voms cms
and then type:
python Common_Settings.py
This script will ask user for providing a
<directory name>. As soon as the jobs get ready, all plots will be sent from Condor inside files called
Results.tar.gz. To untar all files in one go, just type
find /path/to/tar/file/<directory name>/Plot_*/Results.tar.gz | xargs -n1 tar zxvf
where
/path/to/tar/file/ is the location of the
<directory name> in the
ACCESS.
Choosing Event Selections
Basic selections applied to the pair of Tag and Probe muons are:
- |η|Probe < 2.4;
- Tag and Probe of different charges.
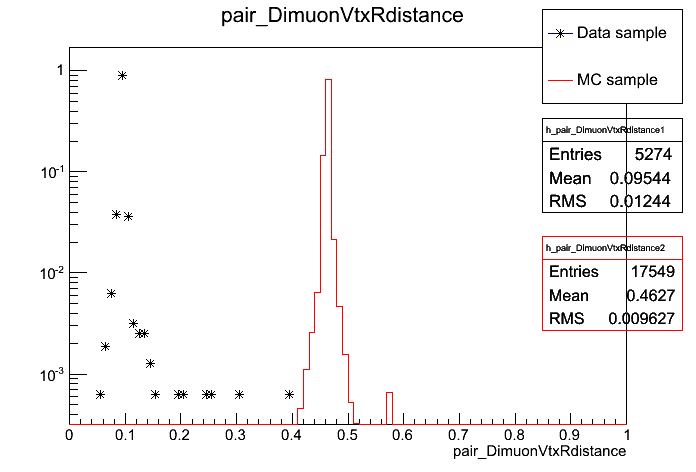
A clear Data vs. MC difference comes from p
T distribution of the Tag muon. From fig. bellow (on the left), a cut of p
T > 45 GeV will be applied to this muon. Figure on the right has a zoom in the region where the cut will be applied to. In a first moment, there is no Data/MC normalization.

Following MuonPOG conveners' suggetion, a cut on the 3D angle between 3-momentum of muons is important to reduce the background from cosmic ray muons. Figures bellow (on the top) show collinearity distributions for Data and MC events with p
T(Tag) > 45 GeV. It has been chosen the same cut used in the
Analysis Note 12-422 (collinearity > 0.02)
(collinearity > 0.02), as mentioned
above
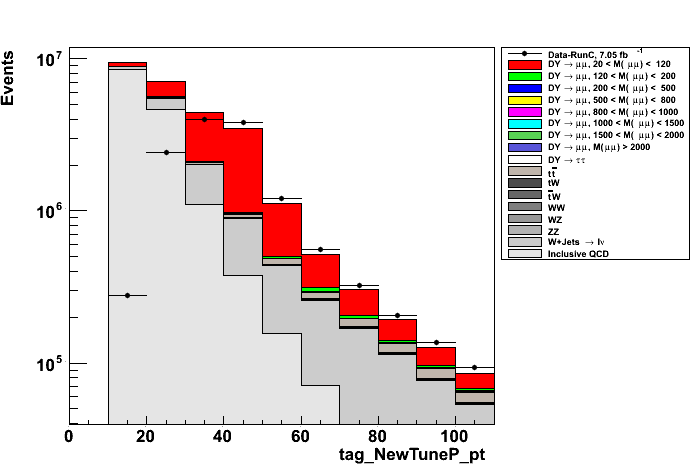
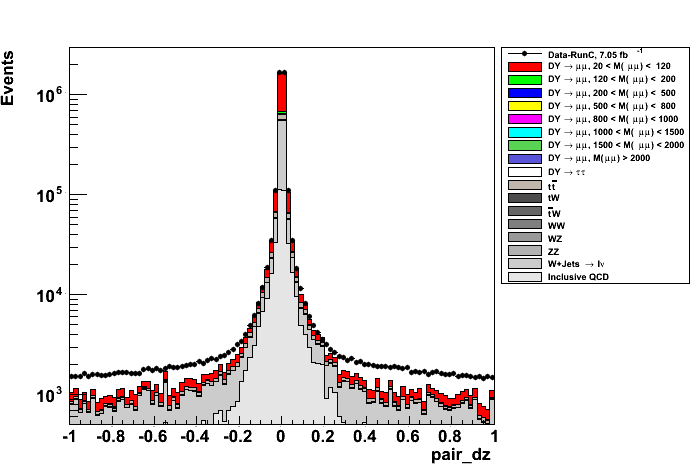
. Figure on the top right has a zoom in the region where the cut will be applied to. MuonPOG conveners have also suggested to apply a tighter cut on the distance of Tag and Probe muons along
z direction in order to improve the capacity of getting muons from the same vertex. Figures on the bottom show the Δz distributions before (left plot) a cut of |Δz| < 0.2 and the χ
2/n.d.f. distribution (right plot) from the vertex fit on the T&P muons after Δz cut.



In summary, all selections applied to pairs of T&P muons, after vertex reweighting, are:
- |η|Probe < 2.4;
- Tag and Probe of different charges;
- pT(Tag) > 45 GeV;
- collinearity > 0.02;
- |Δz| < 0.2 cm;
- χ2/n.d.f. < 10.
Figures bellow compare several distributions of Data and MC events after selections above. No Data/MC normalization has been applied to them.
Common Variables
- invariant mass of Tag and Probe muons (left plot) with zoom between 0 and 1000 GeV (right plot)
- pT of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons
- η of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons
- φ of Tag (left plot) muon and Probe (right plot) muons
- ΔR(μ1,μ2) (left plot) and vertex multiplicity (right plot)
Variables Related to The Vertex Fit
- χ2 / n.d.f. from vertex fit on Tag and Probe muon tracks
- pT of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons from vertex fit (before fit)
- pT of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons from vertex fit (after fit)
- r distance (left plot) w.r.t. beam spot and z coordinate (right plot) from vertex fit on Tag and Probe muon tracks
Additional Variables
- PFCombined isolation of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons
- ∑pT/pT (from inner track fit) of Tag (left plot) and Probe (right plot) muons
- distance between Tag and Probe muons along z direction (left plot) and IsolationR03 ∑pT/pT of Probe muon (right plot)
- collinearity (left plot) and Missing ET (right plot)
Cleaning Up Pairs of Tag and Probe Muons
Now that several selections have been applied to the pairs of T&P muons, ensuring they come from the same vertex and avoiding cosmic ray muons, additional selections have to be taken into account to reject pairs with the following configurations:
- Two Tag-Tag or Probe-Probe muons;
- A second pair of muons where Tag becomes Probe and Probe becomes Tag (should choose that one where pT(Tag) < pT(Probe));
- Pairs of T&P muons which were already taken into account.
In case of having pairs where the Tag makes pairs with different Probes, choose that one with Chi2/NDF closest to "1". This is done using the Chi2 probability, as can be seen
here
.
Here
is a chart flow of the ROOT macro file used to choose the best pair candidates.
New ROOT files containing the new variable (
pair_BestPair) concerning the quality of the muon pairs have been created:
- if is a "good" Tag&Probe pair:
pair_BestPair = 1
- if is a "bad" Tag&Probe pair:
pair_BestPair = 0
Files are located in the
T2_SPRACE storage:
/pnfs/sprace.org.br/data/cms/store/user/adesouza/MuonPOG/HighMassDimuonEff_WithBestPair_Feb_11_2014/
These distributions
check the data/MC agreement after a baseline selection being applied requiring
pair_BestPair = 1. These baseline selections are:
(pair_BestPair == 1) && (charge != tag_charge) && (abs(NewTuneP_eta < 2.4)) && (abs(tag_NewTuneP_eta < 2.4)) && (pair_newTuneP_mass > 20.)
These distributions
now have an additional cut of
pt(Tag) > 45 GeV:
(pair_BestPair == 1) && (charge != tag_charge) && (abs(NewTuneP_eta < 2.4)) && (abs(tag_NewTuneP_eta < 2.4)) && (pair_newTuneP_mass > 20.) && (tag_NewTuneP_pt > 45)
These selections improve the data/MC agreement, but it seems a need to normalize MC samples by a factor of 0.903. Will try other selections...
Computing Efficiencies
Complete

Testing
figures
.
Computing Scale Factors
Complete

Testing Method Back to Z Pole
Complete

Computing Systematic Uncertainties
Complete

Setting Up the Code via GitHub
Complete

Supplementary Material
Complete

Bellow are some links to the relevant CMS web pages and materials for this task.
Meetings, Talks and Additional Materials
- Muon POG Meeting
 : link to the Muon POG meetings held every second Monday (week "A") at 14:00-16:00 (or 16:00-18:00) CET, and every second Thursday (week "A") at 16:00-18:00 CET.
: link to the Muon POG meetings held every second Monday (week "A") at 14:00-16:00 (or 16:00-18:00) CET, and every second Thursday (week "A") at 16:00-18:00 CET.
- Talk on September, 19 2013
 : link to the Muon POG meeting where César and Angelo have given their first presentation about this task. Slides are here
: link to the Muon POG meeting where César and Angelo have given their first presentation about this task. Slides are here .
.
- Recommend new variables
 : these are the slides, sent to the Muon POG conveners in November 2013, comparing Data and MC distributions for several recommended new variables.
: these are the slides, sent to the Muon POG conveners in November 2013, comparing Data and MC distributions for several recommended new variables.
References
-- Main.assantos - 2013-10-26
 A eficiência com que o detector identifica múons é diferente entre eventos de dados reais e eventos simulados. Atualmente essa eficiência é calculada no CMS com base no chamado método “Tag and Probe”, que permite uma performance significativa na identificação de múons através da análise da massa invariante de dois múons de cargas opostas. Contudo, como as buscas por nova Física têm trabalhado com hipóteses que preveem a existência de partículas cada vez mais massiva, e com o acelerador LHC operando a energias cada vez mais altas, observou-se a necessidade da adequação daquele método aos novos cenários.
O LHC colide feixes de prótons a energias de centro de massa consideravelmente altas. Entre 2009 e 2011, o acelerador gerou, progressivamente, colisões de 900, 2.360 e 7000 GeV de energia no centro de massa, chegando a 8.000 GeV em 2012. Atualmente o LHC não está em operação pois passa por uma fase de atualizações com a finalidade de operar a 14.000 GeV, na retomada de funcionamento em 2015, que é a energia para a qual o acelerador foi inicialmente proposto. Colisões próton-próton a energias de centro de massa dessa magnitude tem como resultado a geração de partículas com altos momentos: da ordem de centenas ou, ainda, de milhares de GeV/c.
O momento transversal (pT) das partículas carregadas, que atravessam o detector CMS, é calculado a partir da curvatura de suas trajetórias. Essa curvatura é resultante da interação com um campo magnético de 3.8 Tesla (valor no eixo de simetria do detector) gerado por um solenóide supercondutor. Dentre as partículas carregadas, apenas os múons, cuja massa é de 105 MeV/c², conseguem atravessar todo o detector pois são caracterizados por um tempo de decaimento longo (2,2 μs) e depositam apenas uma pequena fração de sua energia nos calorímetros. É possível calcular o pT de múons pouco energéticos com grande precisão dada a grande curvatura da trajetória que traçam. Por outro lado, a trajetória de múons altamente energéticos desenha um traçado quase retilíneo, diminuindo a precisão na determinação do momento transversal.
O cálculo da eficiência através do método “Tag and Probe” é perfeitamente factível quando os múons estudados apresentam baixos valores de pT, considerando que a reconstrução da massa invariante de duas partículas de cargas opostas, candidatas a múons, resulta mais frequentemente em ressonâncias com baixos valores de massa como os mésons J/Ψ (3,1 GeV/c²) e ϒ (9,5 GeV/c²), e o bóson Z (91,2 GeV/c²). A presença dessas ressonâncias permite selecionar eventos com pares de múons praticamente isolados de ruído. O método “Tag and Probe” consiste em calcular a eficiência na identificação de múons verificando a probabilidade de um dos candidatos a múon (no par) poder ser observado com o perfil do segundo candidato a múon, o qual possui características mais próximas de um múon verdadeiro.
Múons com altos valores de pT, por sua vez, têm maior probabilidade de reconstruir massas invariantes acima de 100 GeV/c² e que estão fora da região onde são observadas as ressonâncias, havendo então a necessidade de adequar o método “Tag and Probe”. Angelo Santos e César Bernardes participam ativamente do Grupo de Múons da colaboração CMS e são responsáveis por desenvolver uma técnica de analise de dados, adaptando o método “Tag and Probe” ao novo cenário, a fim de obter eficiências de múons altamente energéticos para eventos de dados reais e de simulação.
A eficiência com que o detector identifica múons é diferente entre eventos de dados reais e eventos simulados. Atualmente essa eficiência é calculada no CMS com base no chamado método “Tag and Probe”, que permite uma performance significativa na identificação de múons através da análise da massa invariante de dois múons de cargas opostas. Contudo, como as buscas por nova Física têm trabalhado com hipóteses que preveem a existência de partículas cada vez mais massiva, e com o acelerador LHC operando a energias cada vez mais altas, observou-se a necessidade da adequação daquele método aos novos cenários.
O LHC colide feixes de prótons a energias de centro de massa consideravelmente altas. Entre 2009 e 2011, o acelerador gerou, progressivamente, colisões de 900, 2.360 e 7000 GeV de energia no centro de massa, chegando a 8.000 GeV em 2012. Atualmente o LHC não está em operação pois passa por uma fase de atualizações com a finalidade de operar a 14.000 GeV, na retomada de funcionamento em 2015, que é a energia para a qual o acelerador foi inicialmente proposto. Colisões próton-próton a energias de centro de massa dessa magnitude tem como resultado a geração de partículas com altos momentos: da ordem de centenas ou, ainda, de milhares de GeV/c.
O momento transversal (pT) das partículas carregadas, que atravessam o detector CMS, é calculado a partir da curvatura de suas trajetórias. Essa curvatura é resultante da interação com um campo magnético de 3.8 Tesla (valor no eixo de simetria do detector) gerado por um solenóide supercondutor. Dentre as partículas carregadas, apenas os múons, cuja massa é de 105 MeV/c², conseguem atravessar todo o detector pois são caracterizados por um tempo de decaimento longo (2,2 μs) e depositam apenas uma pequena fração de sua energia nos calorímetros. É possível calcular o pT de múons pouco energéticos com grande precisão dada a grande curvatura da trajetória que traçam. Por outro lado, a trajetória de múons altamente energéticos desenha um traçado quase retilíneo, diminuindo a precisão na determinação do momento transversal.
O cálculo da eficiência através do método “Tag and Probe” é perfeitamente factível quando os múons estudados apresentam baixos valores de pT, considerando que a reconstrução da massa invariante de duas partículas de cargas opostas, candidatas a múons, resulta mais frequentemente em ressonâncias com baixos valores de massa como os mésons J/Ψ (3,1 GeV/c²) e ϒ (9,5 GeV/c²), e o bóson Z (91,2 GeV/c²). A presença dessas ressonâncias permite selecionar eventos com pares de múons praticamente isolados de ruído. O método “Tag and Probe” consiste em calcular a eficiência na identificação de múons verificando a probabilidade de um dos candidatos a múon (no par) poder ser observado com o perfil do segundo candidato a múon, o qual possui características mais próximas de um múon verdadeiro.
Múons com altos valores de pT, por sua vez, têm maior probabilidade de reconstruir massas invariantes acima de 100 GeV/c² e que estão fora da região onde são observadas as ressonâncias, havendo então a necessidade de adequar o método “Tag and Probe”. Angelo Santos e César Bernardes participam ativamente do Grupo de Múons da colaboração CMS e são responsáveis por desenvolver uma técnica de analise de dados, adaptando o método “Tag and Probe” ao novo cenário, a fim de obter eficiências de múons altamente energéticos para eventos de dados reais e de simulação.
 The standard T&P technique uses known resonances to help in the selection of true muon pairs. Then in this well described region, i.e., in a mass window around this resonance we select a muon candidate with a considerably tight criteria (high probability to be a true muon - called Tag). Since we need two muons to reconstruct the resonance and we know from numerous previous studies the shape of the dimuon distribution we use fits to select a second muon candidate (called Probe), separating with very good precision muons from background and signal(the resonance). Then we have the Probe, a muon candidate with a high probability to be a true muon and without any tight criteria applied so that we can consider any desirable requeriment to extract its efficiency.
The standard T&P technique uses known resonances to help in the selection of true muon pairs. Then in this well described region, i.e., in a mass window around this resonance we select a muon candidate with a considerably tight criteria (high probability to be a true muon - called Tag). Since we need two muons to reconstruct the resonance and we know from numerous previous studies the shape of the dimuon distribution we use fits to select a second muon candidate (called Probe), separating with very good precision muons from background and signal(the resonance). Then we have the Probe, a muon candidate with a high probability to be a true muon and without any tight criteria applied so that we can consider any desirable requeriment to extract its efficiency. Here
Here :
:  :
:  Before starting trees production, there is a need to add a set of variables we are interested in. These variables are listed in the table bellow.
Before starting trees production, there is a need to add a set of variables we are interested in. These variables are listed in the table bellow.
 Some the variables are include using
Some the variables are include using 

 It is needed to "import" the modules. There is a dedicated module for these purposes in the MuonPOG T&P package. Open the file
It is needed to "import" the modules. There is a dedicated module for these purposes in the MuonPOG T&P package. Open the file  an example of config file to produce Data trees.
an example of config file to produce Data trees.
 Following sub-sections contain:
Following sub-sections contain: 
 These table shows the ROOT file paths of Data and MC samples (MC files with the variable weight).
These table shows the ROOT file paths of Data and MC samples (MC files with the variable weight).


 After vertex reweighting, following sub-sections describe:
After vertex reweighting, following sub-sections describe:  : Users have to apply all necessary changings into this macro. All lines were commented as better as possible.
: Users have to apply all necessary changings into this macro. All lines were commented as better as possible.
 : No need to modify this file. This macro will read all settings defined into
: No need to modify this file. This macro will read all settings defined into  : the script will ask user for providing a directory name which will be created to receive all plots from Condor. In the first part of the code, user can apply all necessary settings to create the plots. The rest of the file takes care of creating a
: the script will ask user for providing a directory name which will be created to receive all plots from Condor. In the first part of the code, user can apply all necessary settings to create the plots. The rest of the file takes care of creating a  : will create a directory called "Processing" and copy the
: will create a directory called "Processing" and copy the  : contains all settings used to run jobs on Condor. An specific flag (
: contains all settings used to run jobs on Condor. An specific flag ( : this script is sent to the nodes, setting up the
: this script is sent to the nodes, setting up the  : this is the same macro files as mentioned above.
: this is the same macro files as mentioned above.

 Following MuonPOG conveners' suggetion, a cut on the 3D angle between 3-momentum of muons is important to reduce the background from cosmic ray muons. Figures bellow (on the top) show collinearity distributions for Data and MC events with pT(Tag) > 45 GeV. It has been chosen the same cut used in the Analysis Note 12-422
Following MuonPOG conveners' suggetion, a cut on the 3D angle between 3-momentum of muons is important to reduce the background from cosmic ray muons. Figures bellow (on the top) show collinearity distributions for Data and MC events with pT(Tag) > 45 GeV. It has been chosen the same cut used in the Analysis Note 12-422


 In summary, all selections applied to pairs of T&P muons, after vertex reweighting, are:
In summary, all selections applied to pairs of T&P muons, after vertex reweighting, are: 



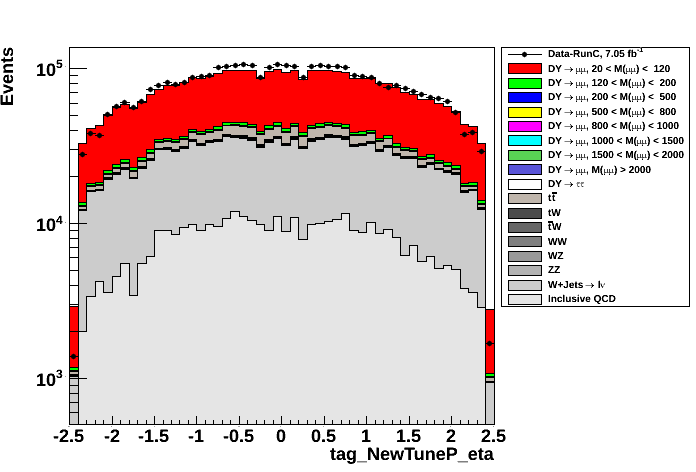

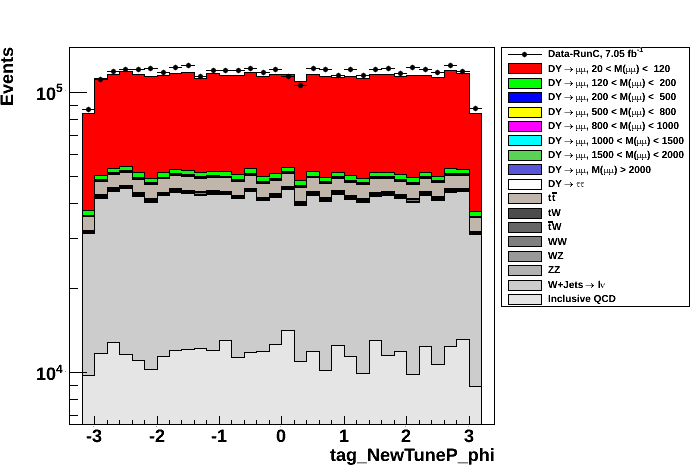


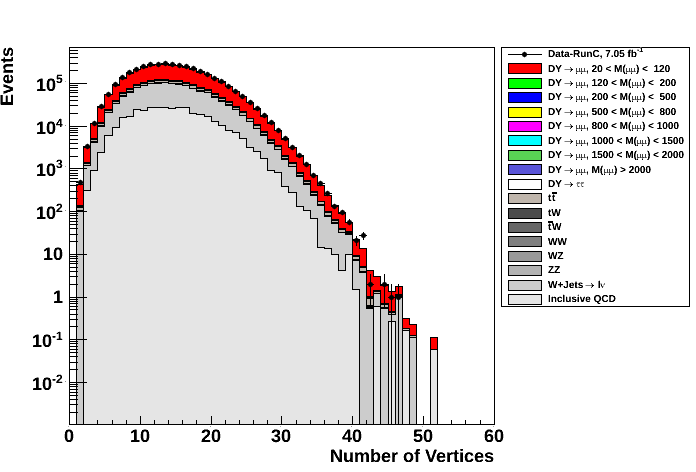
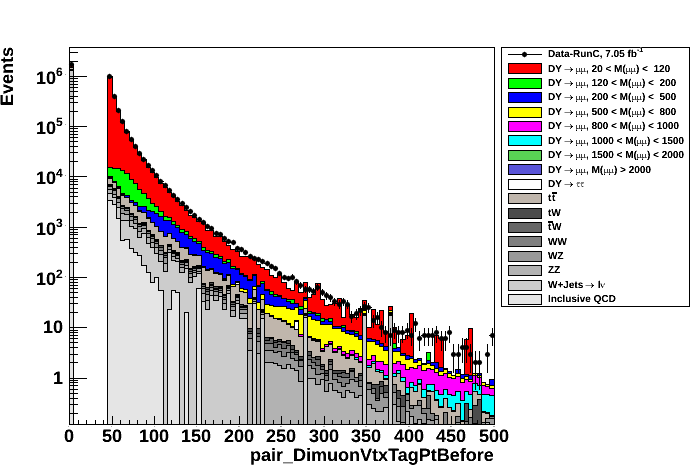
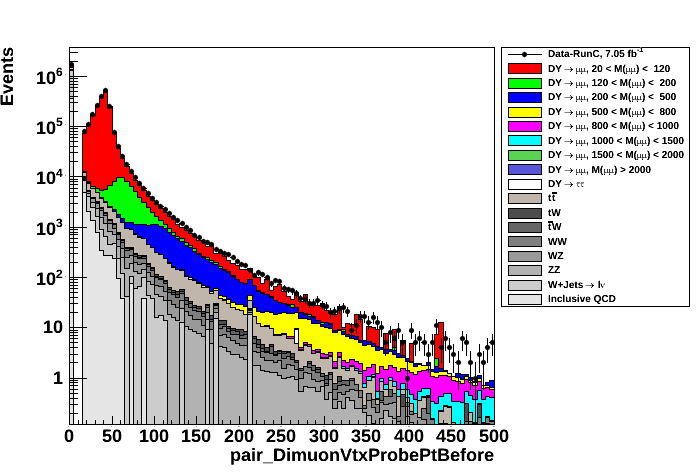


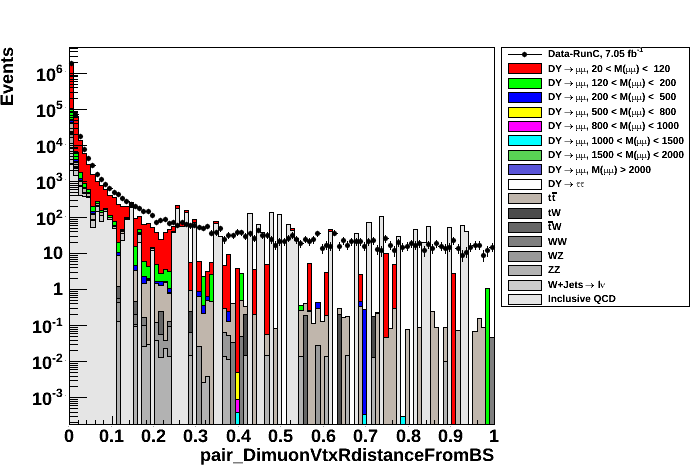


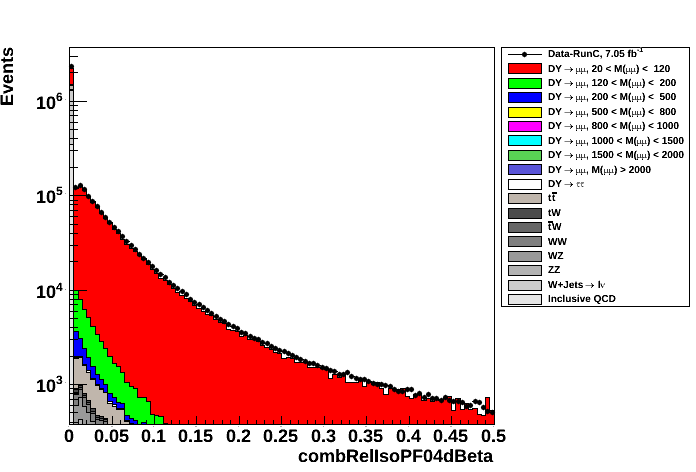
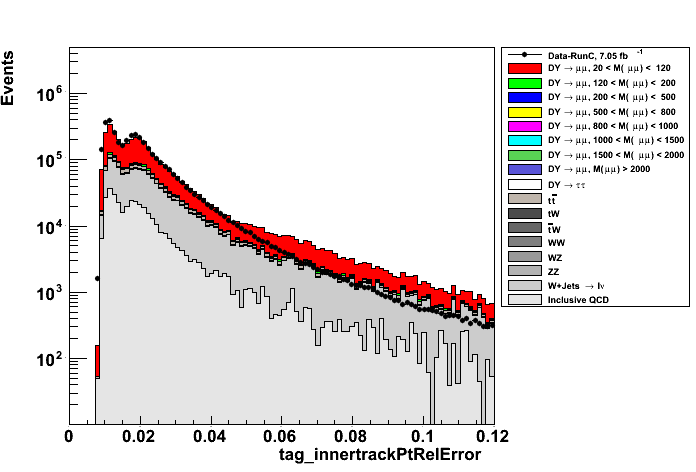

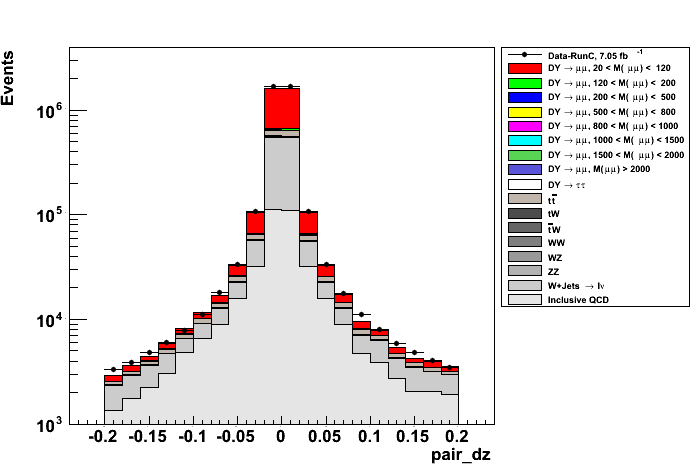
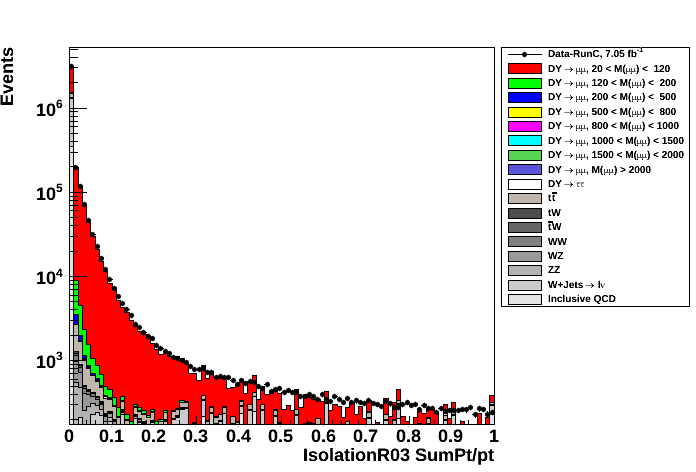


 Testing figures
Testing figures



 Bellow are some links to the relevant CMS web pages and materials for this task.
Bellow are some links to the relevant CMS web pages and materials for this task.
 : link to the Muon POG meetings held every second Monday (week "A") at 14:00-16:00 (or 16:00-18:00) CET, and every second Thursday (week "A") at 16:00-18:00 CET.
: link to the Muon POG meetings held every second Monday (week "A") at 14:00-16:00 (or 16:00-18:00) CET, and every second Thursday (week "A") at 16:00-18:00 CET.
 : link to the Muon POG meeting where César and Angelo have given their first presentation about this task. Slides are here
: link to the Muon POG meeting where César and Angelo have given their first presentation about this task. Slides are here .
.
 : these are the slides, sent to the Muon POG conveners in November 2013, comparing Data and MC distributions for several recommended new variables.
: these are the slides, sent to the Muon POG conveners in November 2013, comparing Data and MC distributions for several recommended new variables.
 : this is the Muon POG web page.
: this is the Muon POG web page.
 : web page of Tag and Probe for muons.
: web page of Tag and Probe for muons.
 : instructions on how to setup the default Tag and Probe code are here.
: instructions on how to setup the default Tag and Probe code are here.
 : this is an Analysis Note of search for Z' from where datasets and instructions concerning veto of cosmic rays were taking from.
: this is an Analysis Note of search for Z' from where datasets and instructions concerning veto of cosmic rays were taking from.
 : here are the instructions to get information of the vertex fit on the Tag and Probe pair.
: here are the instructions to get information of the vertex fit on the Tag and Probe pair.